With a 2015-2016 $90,000 grant from FRAXA Research Foundation, Dr. Herve Moine and Dr. Andrea Geoffroy aim to uncover the exact role of FMRP and to test a novel possible means to correct for FMRP absence in the mouse model of Fragile X syndrome.
Read moreAuthor: FRAXA Research Foundation
Correcting Defects in Astrocyte Signaling in Fragile X Syndrome

With a $90,000 grant from the FRAXA Research Foundation from 2015-2016, Dr. Laurie Doering and Dr. Angela Scott at McMasters University studied astrocytes in Fragile X. Astrocytes, brain cells which support neurons, do not transmit signals. Several treatment strategies for Fragile X have been proposed based on correction of “astrocyte phenotypes”.
Read moreSensory Hypersensibility in Fragile X Syndrome and BK Channel Openers
With $366,100 in grants from FRAXA Research Foundation, these investigators at the University of Orleans studied sensory abnormalities in Fragile X mice and test the ability of a class of drugs, BK channel openers, to rescue these abnormalities.
Read moreFragile X Mutant Mouse Models

With $375,000 in grants from the FRAXA Research Foundation since 2009, Dr. David Nelson has developed an impressive array of advanced mouse models of Fragile X, at Baylor College of Medicine. These models are available to investigators worldwide on request. This resource has been essential for a broad, rapid distribution of Fragile X and related gene mouse models and has increased the pace of Fragile X research.
Read moreMicroRNAs as Biomarkers in Fragile X Syndrome

With a $90,000 grant from FRAXA Research Foundation in 2015-2016, Dr. Mollie Meffert and Dr. Christina Timmerman at Johns Hopkins University studied groups of small RNAs, known as microRNAs, which are greatly decreased in brain tissue of Fragile X mice vs. normal controls.
Read moreRepurposing Drugs to Dampen Hyperactive Nonsense-Mediated Decay in Fragile X Syndrome

With a $90,000 grant from the FRAXA Research Foundation, Dr. Lynne Maquat and Dr. Tatsuaki Kurosaki will investigate nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) in Fragile X. NMD is a “housekeeping” process that cells use to prevent faulty proteins from being made. But there is too much of it in Fragile X syndrome. There are already available drugs that suppress NMD – including caffeine.
Read moreAltered Sleep in Fragile X Syndrome: Basis for a Potential Therapeutic Target

With a $90,000 grant from FRAXA Research Foundation over 2016-2018, Dr. Carolyn B. Smith and Dr. Rache Sare at the National Institute of Mental Health investigated the basis of sleep problems in Fragile X syndrome.
Read moreRolling Stone Magazine: Luke’s Best Chance: One Man’s Fight for His Autistic Son

Rolling Stone Magazine published a powerful article by award-winning writer, Paul Solotaroff, featuring his son, Luke. Luke is 17 years old and has Fragile X syndrome. What will happen when Luke becomes an adult and no longer has a right to schooling? During his research, Paul visited the Shared Living Collaborative in Merrimac, MA. This is the program where my son, Andy, age 28, works (and plays) during his days. Perhaps it can serve as a model for other programs around the country.
Read moreFulcrum Therapeutics Launched with $55 Million to Reactivate the Fragile X Gene

A new company has launched that will invest tens of millions in reactivating the Fragile X gene. With $55 million in investment funds, Fulcrum Therapeutics in Cambridge, MA, aim to develop small molecules to control gene expression. These potential new treatments would be based on controlling genetic on- and off-switches of disease genes. Fulcrum will start with two diseases: Fragile X syndrome and a rare form of muscular dystrophy. FRAXA is funding one of the founding scientists, Jeannie Lee, MD, PhD, of Harvard University, and has been working with others on the new Fulcrum team.
Read moreNew compound from Anavex Improves Learning and Behavior in Fragile X Mice
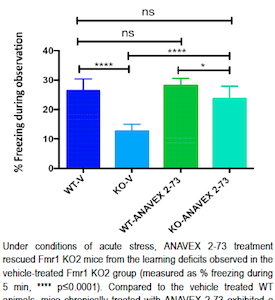
A potential new treatment for Fragile X syndrome is showing promise. While still early in development, the investigational drug was able to improve intellectual, learning and hyperactivity measures in a mouse model of Fragile X syndrome. Anavex 2-73 is a sigma-1 receptor agonist being developed for autism spectrum disorders, including Rett syndrome and Fragile X syndrome, and for Alzheimer’s disease. Anavex Life Sciences presented the data at the Gordon Research Conference for Fragile X and Autism-Related Disorders, held June 5-10, 2016 in Mount Snow, VT. The study was sponsored by FRAXA, via the FRAXA Drug Validation Initiative, and performed by Fraunhofer Chile Research, in Santiago, Chile.
Read moreFragile X Fruit Fly Research Bears Fruit

A new FRAXA-funded study shows how the hormone insulin – usually associated with diabetes — is involved in the daily activity patterns and learning deficits in the fruit fly model of Fragile X Syndrome (FXS). The study also reveal a metabolic pathway that can be targeted by new and already approved drugs to treat Fragile X patients, notably metformin.
Read moreAbnormalities of Synaptic Plasticity in the Fragile X Amygdala

With a $110,050 grant from FRAXA Research Foundation from 2005-2016, Dr. Sumantra Chattarji at the National Center for Biological Sciences researched how the amygdala is affected by Fragile X syndrome. Results published.
Read moreResources for Families: Fragile X – A to Z and Medication Guide

FRAXA Research Foundation is fortunate to attract volunteers and interns from universities far and wide. FRAXA has just four staff on the payroll (three of whom are part time), to keep expenses low and devote your donations to Fragile X research. That also means we are very grateful to our volunteers! This past summer we were joined at the FRAXA Newburyport, MA office by Emily Fluet, a student who had completed her freshman year at the University of St. Andrews in Scotland. Emily has transformed two FRAXA publications into online resources available to all: Fragile X – A to Z and Medication Guide for Fragile X.
Read moreNeuren’s Tofinetide Successful in Phase 2 Clinical Trial in Fragile X
We are pleased to share great news adapted from Neuren’s press release: Neuren’s phase 2 trial has successfully established proof of concept and provides a strong rationale for Neuren to move forward with developing trofinetide for Fragile X syndrome. In this initial small trial with a relatively short treatment period, trofinetide was very well tolerated, with the high dose (70 mg/kg twice daily) demonstrating a consistent pattern of clinical improvement, observed in both clinician and caregiver assessments.
Read moreTargeting AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway in Fragile X Syndrome

With a $100,000 grant from the FRAXA Research Foundation in 2015, Dr. Peter Vanderklish explored a novel strategy to treat Fragile X syndrome: AMPK activators. The good news is that there are FDA approved (for example, metformin) and naturally occurring AMPK activators (such as resveratrol, found in red wine).
Read moreFruit Flies to Model and Test Fragile X Treatments

Dr. Jongens and his collaborators have found an insulin-like protein in the fly brain that is overexpressed in the Fragile X mutant fly, leading to increased activity of the insulin signaling pathway. Furthermore, they found that certain behavioral patterns in the Fragile X flies can be rescued by expressing the FX gene just in insulin producing neurons in the fly brain. In the mutant, there are other changes in the signaling pathways, including a decrease in cAMP and elevation in PI3K, mTOR, Akt and ERK activity. They now propose to study 2 medicines used for diabetes: pioglitazone (increases cAMP and decreases Akt and ERK) and metformin (inhibits mTOR), in flies and mice to validate the potential efficacy of these novel therapeutics for Fragile X.
Read moreAnalysis of Developmental Brain Dysfunction in Families
FRAXA Research Foundation is proud to make a grant of $90,000 over 2014-2015 to Margaret King, PhD. The goal of this project is to identify new approaches to clinical trial design for Fragile X pharmaceuticals.
Read moreCrossroads of Fragile X and Alzheimers Research

Last week researchers at VIB Leuven in Belgium published evidence that a brain pathway involving the protein APP (Amyloid Precursor Protein) plays a vital role in development of Fragile X syndrome, one of the most common causes of autism. Scientists led by Dr. Emanuela Pasciuto in the laboratory of Prof Claudia Bagni published findings of their study in the journal Neuron.
Read moreBoston Bruins Grant Funds New Fragile X Research

Bruins Foundation Executive Director Bob Sweeney pledging a $90,000 donation to FRAXA Research today at Shared Living Collaborative’s Gateway Farm in Merrimac, MA. The award will enable the organization to fund an entirely new research project aimed at developing new treatments for Fragile X, a genetic syndrome that is the most common inherited cause of autism.
Read moreBoston Globe, “Playing a part in finding cure for Fragile X”

Fragile X is rare and not as highly publicized as many other better-known genetic diseases that attract media interest and generate richer revenue streams of giving. The world of the ailing doesn’t prioritize. There is no Find Help 101 manual for funding charities or what makes the public wake up one day and pour out its heart, empty its wallet, join a bike-a-thon for its cure.
Read moreFRAXA Grant to Nahum Sonenberg, PhD — Effects of metformin in Fmr1 knockout mouse model of Fragile X syndrome

Mis-regulation of activity-dependent protein synthesis is one of the major cellular abnormalities found in Fragile X. Upstream neuronal signaling regulates a large cluster of enzymes called the mTORC1 complex, which in turn regulates protein synthesis. This complex is also controlled by cellular energy levels via the metabolic sensor AMP-activated Protein Kinase (AMPK). AMPK is a highly conserved kinase that is activated under conditions of energy stress, when intracellular ATP levels decline and intracellular AMP increases.
Read moreBryostatin Restores Learning and Memory in Adult Fragile X Mice

A bizarre marine critter found off the California coast — Bugula neritina— is the only known source of a potential new Fragile X treatment, Bryostatin. Last month, FRAXA sat down with scientists from Neurotrope BioScience, a specialty biopharmaceutical company developing medicines for rare diseases and Alzheimer’s based on Bryostatin. Their Fragile X program is based on research by a West Virginia team led by Daniel Alkon, MD, which showed that Bryostatin-1 restores hippocampal synapses and spatial learning and memory in adult Fragile X mice.
Read moreFragile X Programs at UMASS – University of MA, Worcester

Fragile X Syndrome Behavioral Health Clinic The Center for Autism and Neurodevelopmental Disorders (CANDO) is opening a specialty clinic for individuals with Fragile X Syndrome (under the direction of Dr. Jean Frazier) to evaluate and provide treatment for behavioral challenges.
Read moreThe Endocannabinoid System in a Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome

With a $128,500 grant over 2011-2013 from FRAXA Research Foundation, Drs. Bradley Alger and Ai-Hui Tang at the University of Maryland researched endocannabinoid pathways in Fragile X.
Read moreInhibitors of STEP as a Novel Treatment of Fragile X Syndrome

With a $349,000 grant from FRAXA Research Foundation from 2008-2015, Dr. Paul Lombroso and his team at Yale University researched if inhibiting STEP could reduce behavioral abnormalities in Fragile X syndrome. Results published.
Read more
