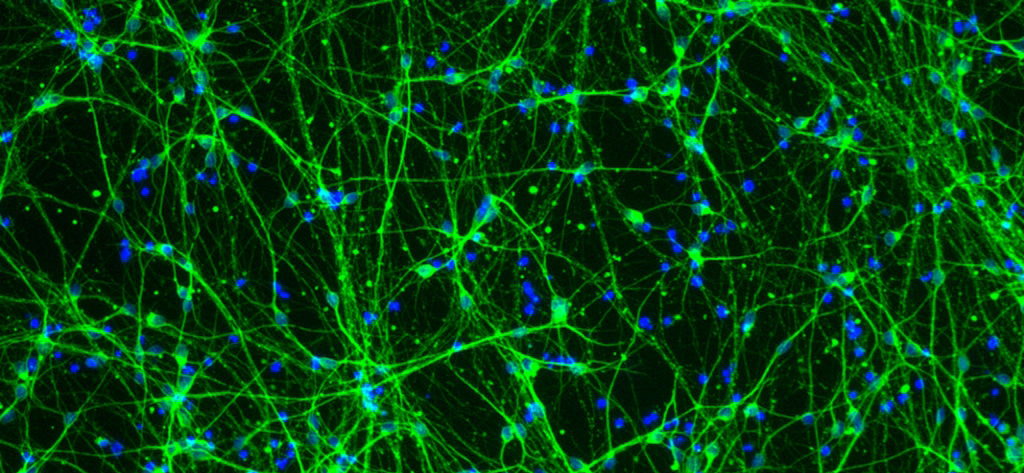
A 2013-2014 FRAXA Research Grant, Synaptic Characterization of Human Fragile X Neurons, has shown that the Fragile X mutation impairs homeostatic plasticity in human neurons, by blocking synaptic retinoic acid signaling.
Principal Investigator Marius Wernig, PhD and FRAXA Postdoctoral Fellow Samuele Marro, PhD at Stanford University used stem cells from human adults, instead of mouse cells, for this study. They found promising results with retinoic acid which is a metabolite of Vitamin A. The system they have developed could provide a powerful new cellular biomarker for screening many treatment approaches.
Dr. Marro provided us with the following summary of results.
Read the published results at Science Translational Medicine
The Fragile X mutation impairs homeostatic plasticity in human neurons by blocking synaptic retinoic acid signaling
Our partial understanding of the molecular mechanisms underling Fragile X syndrome (FXS) is based on animal models, with limitations due to fundamental differences between mice and humans. Human pluripotent stem cells (PSC) have potential to overcome this obstacle but important limitations remain:
- Generation of PSC from patients leads to pronounced line-to-line variability because of different genetic backgrounds of patients and control subjects.
- Current protocols for generating functional neurons from PSC are line-dependent, inefficient and slow.
To address these problems, we established a new genetically engineered FXS model of PSC with homogenous genetic background (isogenic FMR1 conditional knock-out). We used this PSC platform to generate human neurons using transcription factor based protocols developed in our laboratory that are significantly faster and produce mature human neurons with robust synaptic activity.
We observed that human FXS neurons had normal basic functions such as shape, synapses number and synapse activity. However, these Fragile X human neurons entirely lacked a type of synaptic regulation called “homeostatic plasticity.” This is the biological solution that neurons use to stabilize activity in the brain. We also found that the block of homeostatic plasticity in FXS was due to a block of retinoic acid (RA) signaling in both excitatory and inhibitory synapses. Excitingly, we were able to restore RA-mediated homeostatic plasticity in patient-derived neurons using CRISPR-Cas9.
Thus, we established that defective synaptic RA signaling and homeostatic synaptic plasticity are a major synaptic dysfunction in Fragile X syndrome and could impact performance of neural circuits underlying cognitive functions. In addition, our results suggest that FXS PSC – derived neurons might be useful for studying the mechanisms mediating functional abnormalities in FXS.
Finally, this work provides a useful platform for future rigorous drug screenings.
Samuele Marro, PhD - Marius Wernig Laboratory, Stanford University

