Studies at Yale University and elsewhere are showing that FMRP plays a significant role in the regulation of potassium channels. Looking forward, potassium channel opener drugs could rescue some symptoms of Fragile X in humans.
Read moreseizure
Drug Repurposing Study Results Accelerate Progress Towards Fragile X Treatments

While there are over 8,000 rare diseases affecting an estimated 350 million people worldwide, only around 200 of these conditions have effective treatments. Due to the high cost of developing new drugs, rare diseases have historically been less attractive to pharmaceutical companies. Drug repurposing systematically leverages the detailed information available on approved drugs and reduces the time and money needed to deliver safe “new” treatments, but with greater success rates and a potentially more immediate impact on health care.
Read moreIn Their Own Words: Reports From the International Fragile X Workshop

The 18th International Fragile X and Related Neurodevelopmental Disorders Workshop in Quebec, Canada, was a great success, featuring Fragile X much more heavily than any previous meeting in this series! We asked our speakers to summarize their work in their own words, with brief updates from researchers investigating Fragile X.
Read moreClinical Trial of Ganaxolone in Patients with Fragile X Syndrome

With a $90,000 grant from FRAXA Research Foundation funded during 2014-2015, Dr. Frank Kooy and colleagues at the University of Antwerp are conducting a double blind crossover trial of ganaxolone in patients with Fragile X syndrome. Results of this study were mixed (see Marinus: Results from Phase 2 Exploratory Clinical Study Support Continued Development of Ganaxolone in Fragile X Syndrome.)
Read moreNeural Markers of Fragile X: A Powerful New Tool for Clinical Trials
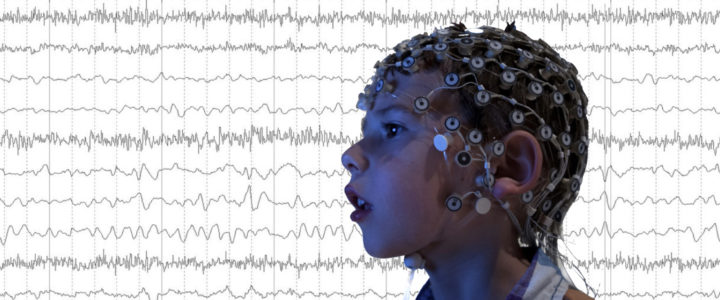
Once the neural marker is identified for a particular challenge, such as kids with poor language versus good language, neural markers can be measured during drug and behavioral therapy trials to see if a child is improving based on objective biological measures.
Read morePreclinical Testing of Sleep-Wake Patterns as an Outcome Measure for Fragile X

FRAXA Research Foundation awarded $122,000 over 2016-2018 to Dr. Cara Westmark at the University of Wisconsin at Madison for studies of sleep disorders in Fragile X syndrome.
Read moreEnhancement of NMDA Receptor Signaling for the Treatment of Fragile X Syndrome

FRAXA Research Foundation funded a 2016-2017 Fellowship for Dr. Stephanie Barnes in the University of Edinburgh lab of Dr. Emily Osterweil. With this $90,000 award, the team is investigating NMDA signaling in fragile X syndrome mice.
Read moreCan STEP Inhibitors Treat Fragile X Syndrome? Yale Professor Investigates

Yale Professor Paul Lombroso, MD, is testing STEP inhibitors to improve cognitive and social behaviors in those affected by Fragile X syndrome.
Read moreFragile X Treatment: New Research Directions
In the wake of negative results from several high-profile clinical trials in Fragile X, we find ourselves questioning many of our previous assumptions about the nature of this disorder. After all, understanding the basic pathology of disease is critical to development of new treatments — this is true across the board, in all branches of medicine.
Read moreThe Endocannabinoid System in a Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome

With a $128,500 grant over 2011-2013 from FRAXA Research Foundation, Drs. Bradley Alger and Ai-Hui Tang at the University of Maryland researched endocannabinoid pathways in Fragile X.
Read moreInhibitors of STEP as a Novel Treatment of Fragile X Syndrome

With a $349,000 grant from FRAXA Research Foundation from 2008-2015, Dr. Paul Lombroso and his team at Yale University researched if inhibiting STEP could reduce behavioral abnormalities in Fragile X syndrome. Results published.
Read moreNIH Awards $35 Million to Three Fragile X Research Teams

The National Institutes of Health has just announced new awards of $35 million over five years to support three Centers for Collaborative Research in Fragile X. Investigators at these centers will seek to better understand Fragile X-associated disorders and work toward developing effective treatments. All of these scientists have been funded for years by FRAXA Research Foundation, and now each team will receive over $2 million per year for five years!
Read moreSeizures in Fragile X Syndrome and Therapeutic Potential of NMDA Receptor Antagonists

With a $90,000 grant from the FRAXA Research Foundation, Dr. Robert Wong is investigating how seizures are generated in Fragile X neurons. More generally, he is looking at how synapses are modified to enable learning and memory and how this process is impaired in Fragile X.
Read morePotassium Channel Modulators to Treat Fragile X

With $246,000 in funding from FRAXA over 2012-2014, the Yale University team of Leonard Kaczmarek, PhD, showed that loss of FMRP leads to an increased Kv3.1 potassium currents and decreased Slack potassium currents in neurons. Both of these changes impair timing of action potentials in auditory neurons (and likely others throughout the brain). The team also found that the firing pattern of neurons in response to repeated stimulation is severely abnormal in Fragile X mice. Based on these results, they are collaborating with the UK-based company Autifony to develop and test advanced compounds which may reverse these deficits.
Read morePreclinical Evaluation of Serotonin Receptor Agonists as Novel Pharmacological Tools in Fragile X Syndrome

With a $66,000 grant from FRAXA Research Foundation in 2013, Dr. Lucia Ciranna and her team from the Universita di Catania tested if specific serotonins could reverse abnormal phentotypes found in Fragile X syndrome.
Read moreAb-Mediated Translation in Fragile X Syndrome

With a $120,000 grant from FRAXA Research Foundation during 2011-2012, Dr. Cara Westmark at the University of Wisconsin explored the role of AbPP as a potential treatment option for fragile X. AbPP produces b-amyloid which is over-expressed in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and Down syndrome.
Read moreInherited Channelopathies in Cortical Circuits of Fmr1 KO Mice

With this two year award of $90,000, Dr. Zhang and Principal Investigator Dr. Andreas Frick at Neurocentre Magendie in France investigated channelopathies using Fragile X mice. Many other proteins are misregulated as a result of the absence of FMRP. It is known that many ion channels, the pores in the cell membrane which allow neurons to conduct electrical impulses, have altered levels in Fragile X. This state is sometime called a “channelopathy” in the pharma world. This group is studying the effect of specific alterations in ion channels, and potential therapeutic effects of drugs which open and close these channels.
Read moreUsing Fenobam to Reduce APP and Abeta in Fragile X Mice

With a $130,000 grant from FRAXA Research Foundation over 2008-2009, Drs. James Malter and Cara Westmark at the University of Wisconsin studied the relationship between the Fragile X protein FMRP and APP, a protein important to the pathology of Alzheimer’s Disease. APP may also contribute to the pathology of Fragile X, and its major metabolite, Aß, may contribute to abnormal protein synthesis via a positive feedback loop. This project sought to restore normal dendritic protein synthesis in Fragile X mice by breaking into this loop.
Read moreTaurine and Somatostatin as Potential Treatments for Fragile X Syndrome: A Unifying Neuro-Endocrine Hypothesis
With a $74,000 grant from FRAXA Research Foundation, Dr. Abdeslem El Idrissi at CUNY explored the GABA receptor system in Fragile X mice and tested somatostatin and taurine as potential therapies for Fragile X; while somatostatin must be infused intravenously, taurine is available as a nutritional supplement.
Read moreDecreased Excitatory Drive onto Parvalbumin-Positive Neocortical Inhibitory Neurons in a Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome

With an $80,000 grant from FRAXA Research Foundation over 2006-7, Drs. Jay Gibson and Kimberly Huber at the University of Texas at Southwestern examined if the defected inhibitory neurotransmission was a primary or secondary symptom of Fragile X to determine where future treatment targets should be focused.
Read moreElectrophysiological, Biochemical and Immunohistochemical Characterization of Kv3.1 in Auditory Brainstem Nuclei in the Fragile X Knockout Mouse

With $80,000 in funding from FRAXA over several years, the Yale University team of Leonard Kaczmarek, PhD showed that loss of FMRP leads to an increased Kv3.1 potassium currents. This change impairs timing of action potentials in auditory neurons (and likely others throughout the brain).
Read moreBaclofen: GABA(B) Receptor Supersensitivity and Normalization of Behavioral Abnormalities by Various GABA(B) Agonists Including Baclofen in FMRP Deficient Mice

With $110,000 in grants from FRAXA Research Foundation over several years, Dr. Miklos Toth from Cornell University discovered increased startle response in Fragile X mice and that baclofen can correct this phenotype.
Read moreProtein Synthesis in Interneurons in Fragile X Mice

With a $100,000 grant from FRAXA Research Foundation from 2004-2006, Dr. Oswald Steward and his team at the University of California studied protein synthesis alterations in Fragile X mice in the brains’ interneurons.
Read moreTherapeutic Interventions in FMR1 Knockout and Transgenic Mice: Role of the FMR1 Gene

With a $229,000 grant from FRAXA Research Foundation in 2006, Drs. Richard Paylor, David Albeck, and Francis Brennan at the Baylor College of Medicine found that, in mice as in humans, the level of Fragile X protein in brain cells plays a prominent role in determining levels of activity and anxiety.
Read moreTransgenic Mouse Models of Fragile X Syndrome

With $736,000 in grants from FRAXA Research Foundation over 2000-2007, Dr. Robert Bauchwitz at Columbia University developed 15 transgenic mouse models of Fragile X syndrome, using them to evaluate a range of experimental treatments. Results published.
Read more
